Difference between revisions of "CI-V interface"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Tested with: IC-706MKIIG, IC-7400 | Tested with: IC-706MKIIG, IC-7400 | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Photos= | ||
=Schematics= | =Schematics= | ||
| + | |||
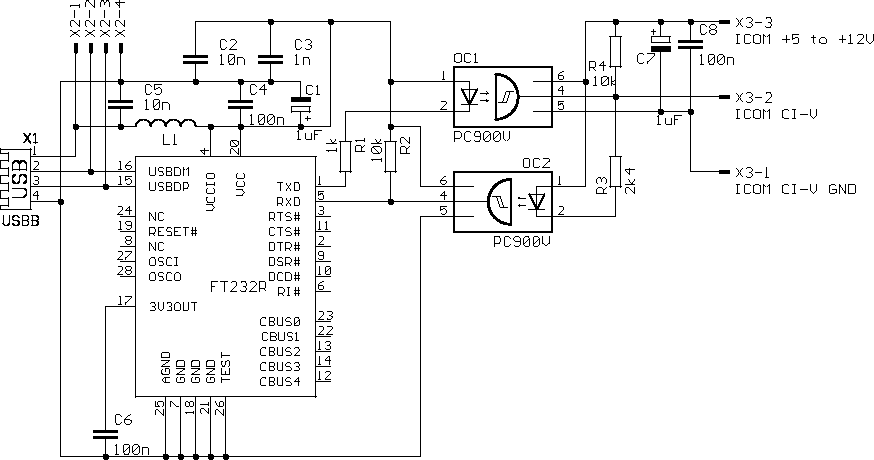
| + | [[Image:Usb2civs120.png|none|frame|Schematics of USB2CIV]] | ||
| + | |||
I've used my favourite USB to serial converter FT232RL in recommended wiring. After many experiments I've found it is not possible to make interface without supply from radio. Radio provides voltage through high impedance. It can work statically but reach real communication speeds is impossible, rise edges are too slow. Supply can be about +5 to +12V . For my purpose best fits +8V from microphone connector (pin 1) next to the CI-V jack. | I've used my favourite USB to serial converter FT232RL in recommended wiring. After many experiments I've found it is not possible to make interface without supply from radio. Radio provides voltage through high impedance. It can work statically but reach real communication speeds is impossible, rise edges are too slow. Supply can be about +5 to +12V . For my purpose best fits +8V from microphone connector (pin 1) next to the CI-V jack. | ||
=PCB= | =PCB= | ||
| − | + | <gallery> | |
| − | + | Image:Usb2civb600.png|PCB of USB2CIV | |
| + | Image:Usb2civoa.png|Parts side A | ||
| + | Image:Usb2civob.png|Parts side B | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 12:33, 21 November 2008
Tested with: IC-706MKIIG, IC-7400
Photos
Schematics
I've used my favourite USB to serial converter FT232RL in recommended wiring. After many experiments I've found it is not possible to make interface without supply from radio. Radio provides voltage through high impedance. It can work statically but reach real communication speeds is impossible, rise edges are too slow. Supply can be about +5 to +12V . For my purpose best fits +8V from microphone connector (pin 1) next to the CI-V jack.